This chapter has a chart, 7 pages long, to help
you find out what disability a child
possibly has, and where to look up that disability
in this book.
If you do not find the sign you are looking for
in the first column, look for another sign. Or
check the signs in the second column.
This chart will help you find out which
disabilities a child might have. It is wise to
look up each possibility. The first page
of each chapter on a disability describes the
signs in more detail.
In addition to this chart, 2 other guides for
identifying disabilities are in this book :
|
IF THE CHILD HAS THIS |
AND ALSO THIS |
HE MAY HAVE |
PAGE# |
SIGNS PRESENT AT OR SOON AFTER
BIRTH
|
|
born weak or 'floppy'
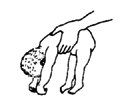
slow to begin to lift head
or move arms.
|
 | often a difficult birth |
 | delayed breathing |
 | born blue and limp |
 | or born before 9 months
and very small |
|
 | cerebral palsy |
 | developmental delay |
|
87
277
|

 | round face |
 | slant eyes |
 | thick tongue |
|
 | Down syndrome
(mongolism) |
 | cretinism |
|
279
282
|

small head, or small top
part of head |
microcephalia (small brain)
mental retardation |
278
|
|
none of above |
developmental delay for
other reasons |
289 |
|
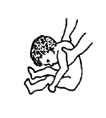
does not suck well or
chokes on milk or food
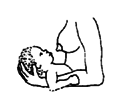
|
 | pushes milk back out
with tongue |
 | or will not suck |
|
cerebral palsy |
87
|
 | cannot suck well |
 | chokes or milk comes
out nose |
|
 | check for cleft
palate
 |
 | possibly severe
retardation |
|
120
277
|
|
one or both feet turned
in or back.
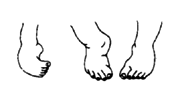
|
no other signs |
club foot |
114
|

 | hands weak, stiff
or clubbed |
 | some joints stiff.
in bent or straight positions |
|
arthrogryposis |
122
|
|
dark lump on back |
spina bifida |
167
|
|
'bag' or dark lump on
back

|
 | clubbed feet
 |
 | or feet bend up too
far |
 | or feet lack
movement and feeling |
|
spina bifida
(sometimes no 'bag' is seen, but foot
signs may be present) |
167
|
 head
too big; keeps growing. head
too big; keeps growing.
|
may develop:

 | eyes like
'setting sun' |
 | increasing mental
and/or physical disability |
 | blindness |
|
hydrocephalus (water on
the brain) |
169
|
|
At birth, this is
usually a sign of spina bifida. |
167
|
|
in an older child,
possibly tapeworm in brain, or a brain
tumor |
WTND
143
|
 upper
lip and/or roof of mouth incomplete. upper
lip and/or roof of mouth incomplete.
|
 | difficulty
feeding |
 | later, speech
difficulties |
|
 | cleft lip (hare
lip) |
 | and cleft palate |
|
120
|
|
birth deformities,
defects, or missing parts.

|
(may or may not be
associated with other problems) |
See
 | birth defects |
 | amputations |
 | Down syndrome |
 | developmental
delay |
|
119
227
279
287
|
|
abnormal stiffness or
position.
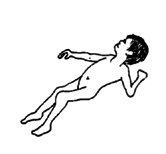 |
 | from birth |
 | some muscles
weak |
 | some joints
stiff |
 | head control
and mind normal |
|
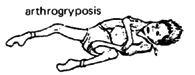
arthrogryposis |
122
|
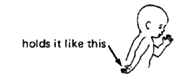
 | Muscles tighten
more in certain positions. |
 |
 may grip thumb tightly
may grip thumb tightly |
|
spastic cerebral
palsy
Note:
muscle tightness (spasticity)
usually does not appear until weeks
or months after birth. |
89
|
|
053
|
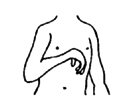 one
arm weak or in strange position one
arm weak or in strange position
|
does not move the arm
much
|
Erb's palsy (weakness
from damage to nerves in shoulder
during birth) |
127
|
|
leg on same side
often affected |
hemiplegic
(one-sided) cerebral palsy |
90
|
|
dislocated hip at
birth.
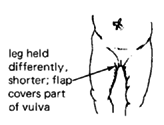
|
On opening legs like
this, leg 'pops' into place or does
not open as far.
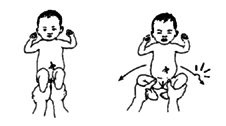
|
dislocated hip from
birth (often both hips)
may be present with:
 | spina bifida |
 | Down syndrome |
 | arthrogryposis |
Also see
Page 156. |
155
167
279
122
|
 slow
to respond to sound or to look at
things slow
to respond to sound or to look at
things |
(may be due to one
or a combination of problems) |
Check for signs of:
 | developmental
delay |
 | cerebral
palsy |
 | blindness |
 | deafness |
|
290
87
243
257
|
SIGNS IN CHILDREN
|
|
slower than other
children to do things (roll,
sit, use hands, show interest,
walk, talk)
|
slow in most or
all areas: |
Developmental
delay, check for signs of: |
287
|

 | round face |
 | slant eyes |
 | single deep
crease in hand |
|
Down syndrome
(mongolism) |
279
|

 | movements
and response slow |
 | skin dry
and cool |
 | hair often
low on forehead |
 | puffy
eyelids |
|
cretinism |
282
|
has continuous
strange movements positions,
and/or stiffness
 |
cerebral palsy
also cheek for:
 | blindness |
 | deafness |
 |
malnutrition |
|
87
243
257
320
|
|
does not
respond to sounds, does not
begin to speak by age 3

|
may respond to
some sounds but not others
Check for ear infection (pus). |
Check for:
 | deafness |
 | severe
developmental delay (with or
without deafness) |
 | severe
cerebral palsy |
|
257
283
87
|
|
does not turn
head to look at things, or
reach for things until they
touch her
|
Eyes may or
may not look normal. |
 |
blindness and/or |
 | severe
mental retardation |
 | severe
cerebral palsy |
|
243
277
87
|
|
Eyelids or
eyes make quick, jerky, or
strange movements.

|
Check for
one or a combination of
these. |
 |
blindness |
 | fits |
 | too
much medicine |
 |
cerebral palsy |
 | other
problems affecting or
damaging the brain |
|
243
233
15
87
14
|
|
054
|
|
All or
part of body makes
strange, uncontrolled
movements.
|
 |
begins suddenly, child
may fall or lose
consciousness |
 |
child is normal (or
more normal) between
'fits' |
|
epileptic
fits
(Pattern varies a lot in
different children-or
even in the same child.) |
233
|
slow, sudden, or
rhythmic movements;
fairly continuous
(except in sleep);no
loss of consciousness |
athetoid cerebral
palsy
(Note:
Fits and cerebral
palsy may occur in the
same child.) |
89
|
|
Body,
or parts of it,
stiffens when in
certain positions:
poor control of some
or all movements. |

 |
different positions
in different
children |
 |
Body may stiffen
backward and legs
cross. |
|
spastic
cerebral palsy |
89
|
PARTS OF
BODY WEAK OR PARALYZED
|
|
IF THE
CHILD HAS THIS |
AND
ALSO THIS |
HE MAY
HAVE |
SEE PAGE |
|
floppy
or limp
weakness in part or
all of body
no loss
of feeling
in affected parts
no
spasticity
(muscles that tighten
without control)
normal
at birth
|
 |
usually began with a
'bad cold and fever
before age 2 |
 |
irregular pattern of
parts weakened.
Often one or both
legs-sometimes arm,
shoulder, hand, etc. |
|
polio |
59
|
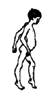
 |
begins little by
little and
steadily gets
worse |
 |
about the same on
both sides of body |
 |
often others in
the family also
have it |
|
 |
muscular atrophy |
 |
muscular atrophy |
|
109
112
|
 |
Paralysis starts
in legs and
moves up; may
affect whole
body. |
 |
or, pattern of
paralysis
variable |
|
tick paralysis

Guillain-Barre'
paralysis (usually
temporary)
paralysis from
pesticides,
chemicals, foods (lathyrism) |
not in book
62
15
|
|
lump on back (See
Page 57.) |
tuberculosis of
spine |
165
|
|
floppy or limp
weakness
usually
some loss of
feeling |
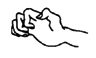
 |
one or both
hands or feet |
 |
develops
slowly in
older child.
Gets worse and
worse. |
|
leprosy |
215
|
 |
born with bag
on back (Look
for scar.) |
 |
feet weak,
often without
feeling |
|
spina bifida |
167
|
 |
usually from
back or neck
injury
weakness, loss
of feeling
below level of
injury |
 |
may or may not
have muscle
spasms |
 |
loss of
bladder and
bowel control |
|
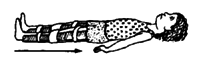
spinal cord
injury
|
175
|
|
injury to nerves
going to one
part of body |
hand weakness
sometimes caused
by using
crutches wrongly |
393
|
|
055
|
|
weakness usually
with stiffness
or spasticity of
muscles
no loss of
feeling |
usually affects
body in one of
these patterns
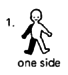
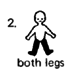

Muscles tighten
and resist
movement because
of joint pain. |
 |
1: cerebral
palsy (or
stroke,
usually older
persons) |
 |
2 and 3:
cerebral palsy |
 |
occasional
other causes |
JOINT PAIN
(many causes-see
below) |
87
130
|
JOINT PAIN
|
|
IF THE CHILD
HAS THIS |
AND ALSO THIS |
HE MAY HAVE |
SEE PAGE |
|
one or more
painful joints |
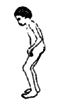
 |
begins with
or without
fever |
 |
gradually
gets worse,
but there
are better
and worse
periods |
|
juvenile
arthritis |
135
|
| |
other causes
of joint pain
See chart on
joint pain. |
130
|
WALKS WITH
DIFFICULTY OR
LIMPS
|
|
dips to one
side with each
step

|
one leg often
weaker and
shorter |
Check for:
 |
polio |
 |
cerebral
palsy |
 |
dislocated
hip |
|
59
87
155
|
 |
usually
begins age
4 to 8 |
 |
may
complain
of knee
pain |
|
damaged hip
joint |
157
|
|
walks with
knees
pressed
together
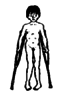
|
 |
muscle
spasm and
tightness |
 |
upper body
little
affected |
|
spastic
diplegic or
paraplegic
cerebral
palsy |
87
|
|
stands and
walks with
knees
together and
feet apart

no other
problems |

feet less
than 3"
apart at age
3 |
normal from
ages 2 to 12 |
113
|

feet more
than 3"
apart at age
3 |
knock-kneed |
114
|
|
walks
awkwardly
with one
foot tiptoe

|
muscle
spasms and
poor control
on that
side. Hand
on that side
often
affected. |
hemiplegic
cerebral
palsy |
90
|
|
(stroke in
older
persons) |
not in
book |
|
walks
awkwardly
with knees
bent and
legs usually
separated

|
jerky steps,
poor balance
sudden,
uncontrolled
movements
that may
cause
failing |
athetoid
cerebral
palsy |
89
|
|
slow
'drunken'
way of
walking
learns to
walk late
and falls
often |
 |
poor
balance
(ataxia)-often
with
cerebral
palsy |
 |
Down
syndrome
(mongolism) |
 |
cretinism |
|
90
279
282
|
|
walks with
both feet
tiptoe

|
 |
weakness,
especially
in legs
and feet |
 |
gradually
gets
worse
and
worse |
|
muscular
dystrophy |
109
|
|
legs and
feet
stiffen
(spasticity
of muscle) |
spastic
cerebral
palsy |
89
|
|
no other
problems |
normal?
(some
normal
children
at first
walk on
tiptoes) |
292
|
|
056
|
|
walks with
hand(s)
pushing
thigh(s)
or with
knee(s)
bent back
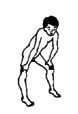
|
|
 |
polio |
 |
muscular
dystrophy |
 |
arthritis
(joint
pain) |
 |
other
causes
of
muscle
weakness |
|
59
109
135
112
|
|
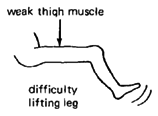
Foot
hangs
down
weakly
(foot
drop).
|
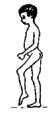
Child
lifts
foot
high
with
each
step so
that it
will not
drag. |
 |
polio |
 |
spina
bifida |
 |
muscular
dystrophy |
 |
muscular
atrophy |
 |
nerve
or
muscle
injury |
 |
other
cause
of
weakness |
|
59
167
109
112
35
139
|
|
dips
from
side
to
side
with
each
step
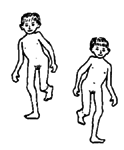
|
due to
muscle
weakness
at
side
of
hips,
or
double
dislocated
hips,
or
both |
 |
polio |
 |
cerebral
palsy |
 |
spina
bifida |
 |
Down
syndrome |
 |
muscular
dystrophy |
 |
child
who
stays
small |
 |
arthrogryposis |
 |
dislocated
hips
(may
occur
with
any
of
the
above) |
|
59
87
167
279
109
126
122
155
|
|
walks
with
one
(or
both)
hip,
knee,
or
ankle
that
stays
bent
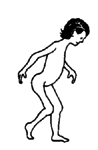
|
joints
cannot
be
slowly
straightened
when
child
relaxes
(see
page
79). |
 |
contractures
(shortened
muscles) |
 |
joined
or
fused
joints |
may
be
secondary
to:
 |
polio |
 |
joint
infection |
 |
other
causes |
|
77
80
59
131
231
|
|
Joints
can
gradually
be
straightened
when
child
relaxes. |
spasticity,
often
cerebral
palsy |
89
|
|
Knees
wide
apart
when
feet
together
(bow
legs).
Waddles
or
dips
from
side
to
side
(if
he
walks).

|
under
18
months
old |
often
normal |
113
|
|
Any
combination
of
these:
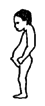
 | Joints look big or thick. |
 | Child is short for age. |
 | Bones weak, bent, or break easily. |
 | Arms and legs may seem too short for body, or 'out of proportion'. |
 | Belly and butt stick out a lot. |
|
Consider:
 | rickets (lack of vitamin D and sunlight) |
 | brittle bone disease |
 | children who stay very short (dwarfism) |
 | cretinism |
 | Down syndrome |
 | dislocated hips |
|
125
125
126
282
279
155
|
| flat feet 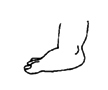
|
no pain or other problems |
normal in many children |
113 |
 | Pain may occur in arch of foot. |
 | Deformity may get worse. |
|
may be problems in:
 | cerebral palsy |
 | polio |
 | spina bifida |
 | Down syndrome |
|
87
59
167
279 |
BACK CURVES AND DEFORMITIES
|
| sideways curve of backbone 
|
When child bends over, look for a lump on one side. 
|
'scoliosis' - may occur alone or as complication of: polio cerebral palsy muscular dystrophy spina bifida other physical disability |
59
87
109
167
162 |
| 057 |
| swayback 
|
 | belly often sticks out |
 | may be due to contractures here, or weak stomach muscles |
|
'lordosis' - may occur in:
 | polio |
 | spina bifida |
 | cerebral palsy |
 | muscular dystrophy |
 | Down syndrome |
 | cretinism |
 | child who stays small many other disabilities |
|
59
167
87
109
279
282
126
161 |
| rounded back 
|
|
'kyphosis' - often occurs with:
 | arthritis |
 | spinal cord injury |
 | severe polio |
 | brittle bone disease |
|
136
175
59
125 |
| hard, sharp bend of or bump in backbone 
|
 | starts slowly and without pain |
 | often family history of tuberculosis |
 | may lead to paralysis of lower body |
|
tuberculosis of the spine |
165 |
| dark soft lump over backbone 
|
 | present at birth |
 | sometimes only a soft or slightly swollen area over spine |
 | weakness and loss of feeling in feet or lower body |
|
spina bifida ('sack on the back') |
167 |
OTHER DEFORMITIES
|
| missing body parts |

born that way |
born with missing or incomplete parts |
121 |

accidental or surgical loss of limbs (amputation) |
amputations |
227 |

gradual loss of fingers, toes, hands, or feet, often in persons who lack feeling |
 | osteomyelitis (bone infections) |
sometimes seen with
 | leprosy (hands or feet) |
 | spina bifida (feet only) |
|
159
215
167 |
| hand problems (For hand problems from birth, see Page 305) |
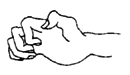
 | floppy paralysis (no spasticity) |
 | without care may lead to contractures so that fingers cannot be opened |
|
may occur with:
 | polio |
 | muscular dystrophy |
 | muscular atrophy |
 | spinal cord injury (at neck level) |
 | leprosy |
 | damage to nerves or cords of arms |
All may lead to contractures. |
59
109
112
175
215
127 |
 
 | uncontrolled muscle tightness (spasticity) |
 | strange movements |
 | or hand in tight fist |
|
spastic cerebral palsy may lead to contractures |
89 |

burn scars and deformities |
burns |
231 |
| clubbing or bending of feet (For club feet from birth, see Page 114.) |
may begin as floppy weakness and become stiff from contractures, if not prevented 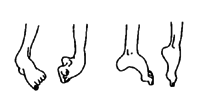
|
may occur with many physical disabilities, including:
 | polio |
 | cerebral palsy |
 | spina bifida |
 | muscular dystrophy |
 | arthritis |
 | spinal cord injury |
|
59
87
167
109
139
175 |
| 058 |
DISABILITIES THAT OFTEN OCCUR WITH
OR ARE SECONDARY TO OTHER DISABILITIES
|
| Developmental delay: child slow to learn to use her body or develop basic skills 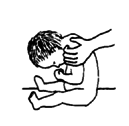
|
caused by slow or incomplete brain function or by severe physical disability, or both |
often seen in:
 | mental retardation |
 | cerebral palsy |
 | severely or multiply disabled children |
|
277
87
283 |
| caused by overprotection: treating children like babies when they could do more for themselves |
some delay can occur with almost any disability |
287 |
Contractures joints that no longer straighten because muscles have shortened
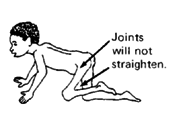
|
 | usually due to muscle weakness or spasticity |
 | Often, muscles that pull a joint one way are much weaker than those that pull it the other way (muscle imbalance). |
|
often secondary to:
 | polio |
 | cerebral palsy |
 | spina bifida |
 | arthritis |
 | muscular dystrophy |
 | Erb's palsy |
 | amputations |
 | leprosy |
|
59
87
167
135
109
127
227
215 |
| sometimes due to scarring from burns or injuries |
burns |
231 |
| Behavior problems
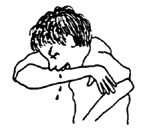
|
may come from:
 | brain damage |
 | difficulty understanding things |
 | overprotection |
 | difficult home situation |
(Some children with epilepsy from brain damage may pull out hair, bite themselves, etc.) |
behavior problems common with:
 | mental retardation |
 | fits (epilepsy) |
 | cerebral palsy |
and for emotional reasons, with:
 | spinal cord injury |
 | muscular dystrophy |
 | deafness |
 | learning disability |
|
277
233
87
175
109
257
365 |
| Slow to learn certain things only; otherwise intelligent. |
 | often over-active or nervous |
 | sometimes behavior problems |
|
learning disability |
365 |
| Speech and communication problems |
 | often, but not always, due to deafness or retardation (or both) |
 | Some children can hear well and are |

but still cannot speak. |
may occur with:
 | deafness |
 | developmental delay |
 | cerebral palsy |
 | Down syndrome |
 | cretinism |
 | children who stay small |
 | brittle bone disease |
 | cleft lip and palate |
(Deafness may occur together with these and other disabilities.) |
257
287
87
279
282
126
125
120 |
| other problems that sometimes occur secondary to other disabilities (Some of these we have already included in this chart.) |
Main disability
 | cerebral palsy |
|
Common secondary disabilities
|
243
257
233 |
 | many disabilities with paralysis |
|
 | spinal curve |
|
161 |
 | persons who have lost feeling: leprosy, spinal cord injury, spina bifida |
|
 | pressure sores |
 | osteomyelitis (bone infection) |
 | loss of urine and bowel control |
|
195
159
203 |










 head
too big; keeps growing.
head
too big; keeps growing.
 upper
lip and/or roof of mouth incomplete.
upper
lip and/or roof of mouth incomplete.



 may grip thumb tightly
may grip thumb tightly one
arm weak or in strange position
one
arm weak or in strange position



 slow
to respond to sound or to look at
things
slow
to respond to sound or to look at
things






















































